Heapsort
The heap data structure
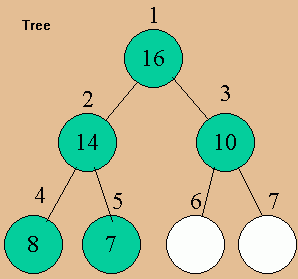
Binary Heap: Array that can be viewed as a complete binary tree. The tree is completely filled except for (perhaps) the lowest level.
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
2 |
3
|
4
|
5
|
| 16 |
14 |
10 |
8 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Array |
: A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Attributes of A:
- Length [A] ³ heap-size [A]
- A [1...length[A]] may be defined, but A [1...heap-size[A]...length[A]] contains the heap.
- A [1] is the root.
- Parent (i) returns ë i/2 û --
a
right one bit shift
- left (i) returns 2 i -- a left one bit shift by i
- right (i) returns 2 i + 1 -- a left one bit shift by i and shifting in a low-order bit 1
Heaps have the heap property:
A [ parent (i) ] ³ A [ i ] (other than the root)
Heaps have the largest element in the root. Subtrees have smaller elements then where rooted. The height of a node in a heap is defined as the length of the longest path to the bottom. The height of the heap is the height of the root.
If n = heap-size of A then height of A is Q ( lg n ) because the heap is basically a binary tree.
|







